Wisconsin remains a global manufacturing center in line with other Great Lakes States.
Industry clusters are regional concentrations of related industries.[i] Clusters consist of companies, suppliers, and service providers, as well as government agencies and other institutions that provide education, information, research, and technical support to a regional economy.[ii] Clusters are a network of economic relationships that create a competitive advantage for the related firms in a particular region, and this advantage then becomes an enticement for similar industries and suppliers to those industries to develop or relocate to a region.[iii] Clusters exist in all types of economies and are more prevalent in locations that achieve better performance relative to their overall stage of development.[iv] It is useful to view economies through the lens of clusters rather than specific types of companies, industries, or sectors because clusters capture the important linkages and potential spillovers of technology, skills, and information that cut across firms and industries.[v] Viewing a group of companies and institutions as a cluster highlights opportunities for coordination and mutual improvement.
A Location quotient is an indicator of the economic concentration of a certain industry in a state, region, county, or city compared to a base economy, such as a state or nation that measures industry clusters in a region. A location quotient greater than 1 indicates the concentration of that industry in the area. A location quotient greater than 1 typically indicates an industry that is export oriented. An industry with a location quotient of 1 with a high number of jobs present is likely a big exporter and is bringing economic value to the community feeding the retail trade and food services sectors.
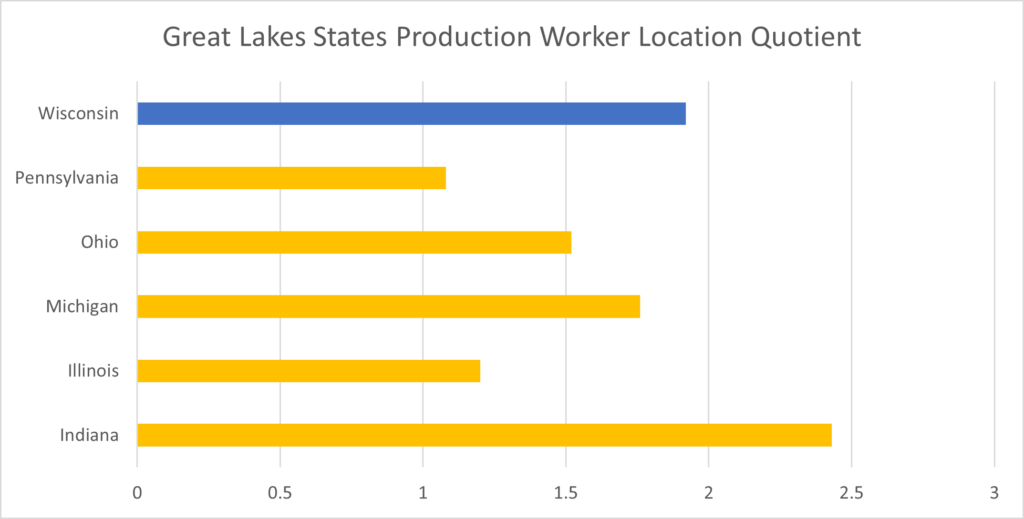
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
As the table above illustrates, the Great Lakes states all have a higher-than-average number of manufacturing production jobs with Wisconsin only behind Indiana which is the nation’s number one manufacturing state on a per capita basis.
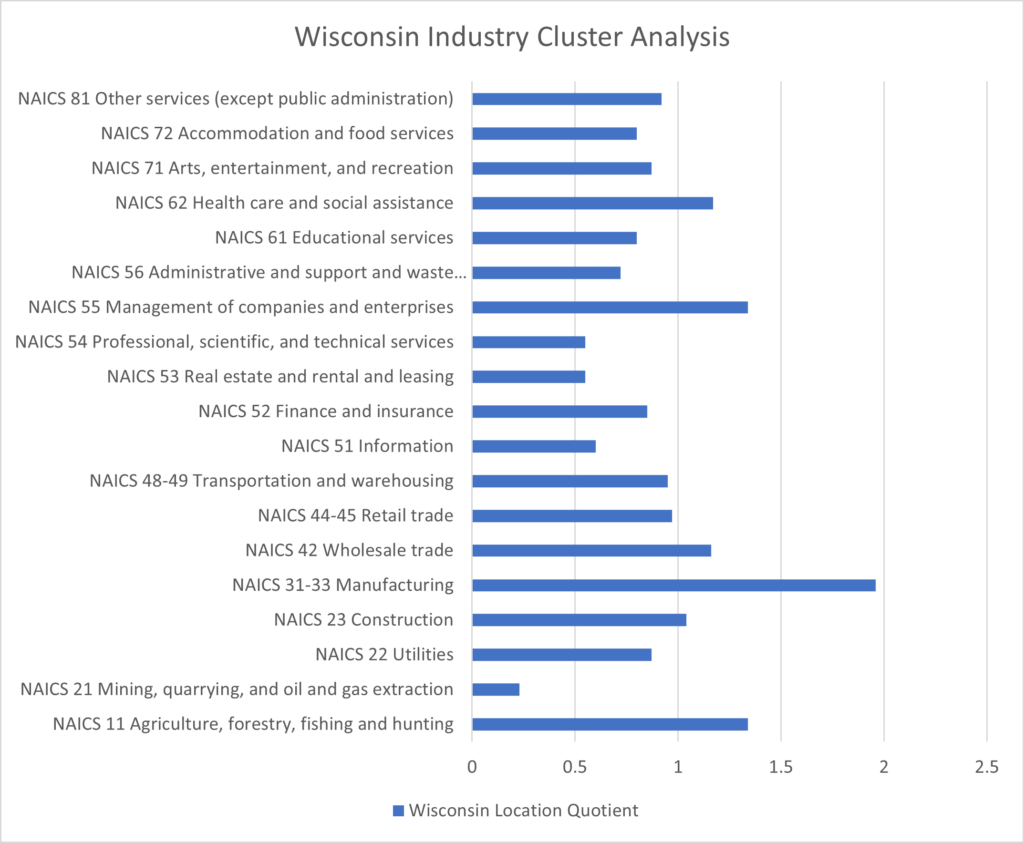
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
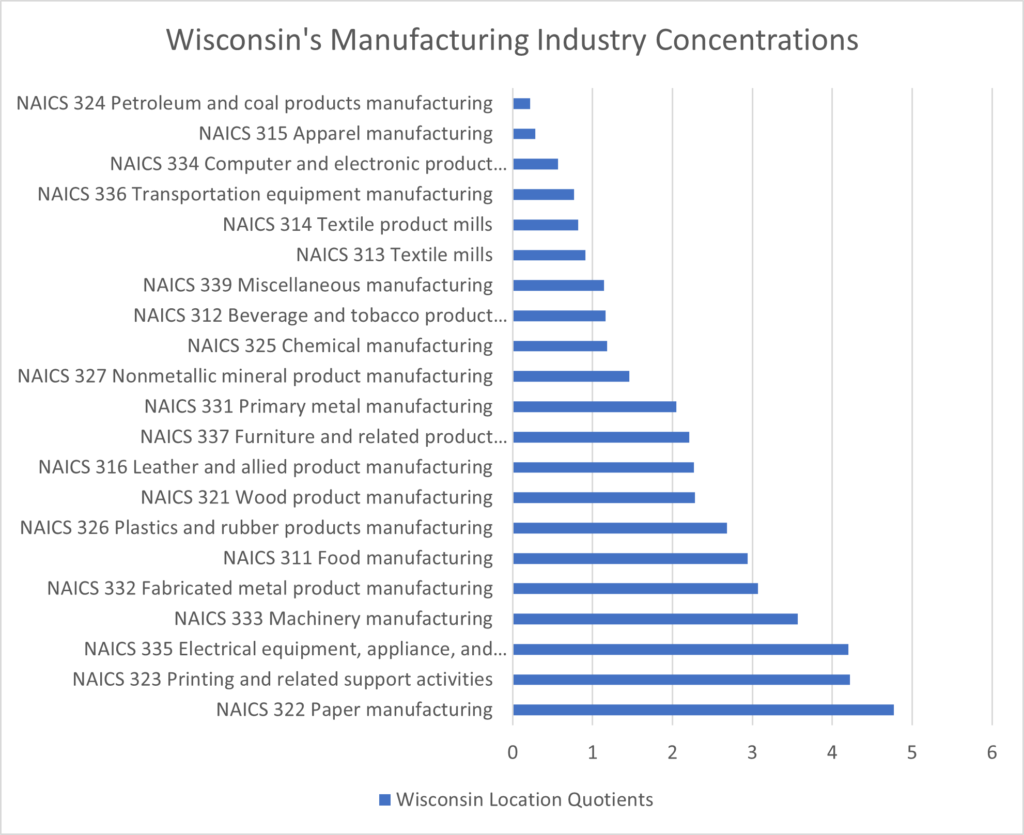
The state of Wisconsin continues to be a leader not just in manufacturing but also in health care, company management, wholesale trade as well as agriculture as illustrated by the table above. The chart below analyzes Wisconsin’s manufacturing industry strengths. Wisconsin is home to over 11 manufacturing industry sectors that more than double the industry average for the location of jobs and wages. These industries include:
- Printing and related support activities
- Electrical equipment, appliance, and component manufacturing
- Machinery manufacturing
- Fabricated metal product manufacturing
- Food manufacturing
- Plastics and rubber products manufacturing
- Wood product manufacturing
- Leather and allied product manufacturing
- Furniture and related product manufacturing
- Primary metal manufacturing.
A review of Milwaukee’s top occupations illustrates again the important role manufacturing, education, advanced services, and healthcare play in this region as all these industries are above the national average with employees in the Milwaukee region. The Milwaukee MSA has over 113,000 workers in the manufacturing sector paying an average wage of $77,000. Milwaukee remains a manufacturing center aligned with its heritage and in common with other Great Lakes major mid-sized urban markets.
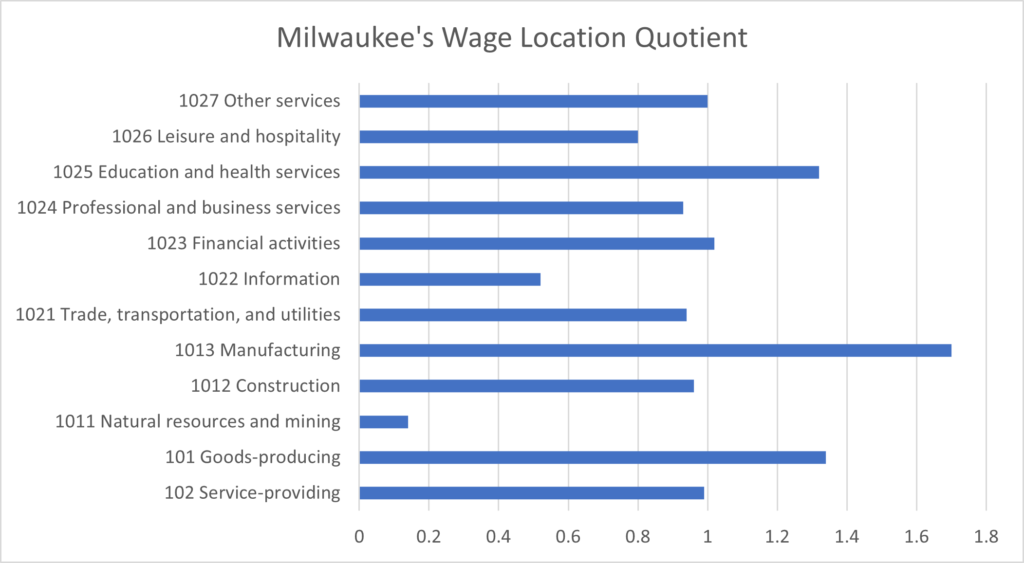
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Milwaukee and the state of Wisconsin remain an industrial powerhouse building on a strong legacy of manufacturing prowess.
[i] https://www.ibrc.Illinois.edu/ibr/2015/spring/article2.html
[ii] Ibid.
[iii] Ibid.
[iv] https://clustermapping.us/content/clusters-101
[v] Ibid.