Global companies seeking a corporate site location in the United States need target markets with like industries, quality sites, a job-ready workforce and a competitive cost of doing business.
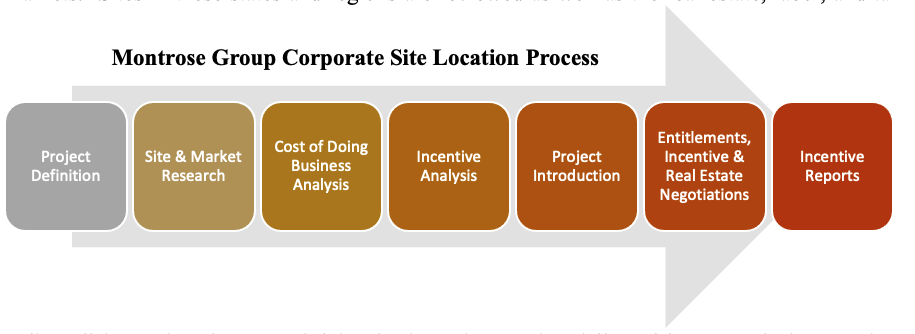
The corporate site location process begins with defining the project to learn about the industry, the number of jobs, payroll, and capital investment planned by a company, needs for the project site, and geographic markets that fit the company’s business plan leading to the creation of potential state and regional target list for the company’s location. Next, market research begins to understand the economic analysis of growth, industry cluster, labor shed, transportation, infrastructure, and supply chain of an industry, company, and region and potential real state options for each of these markets. Sites in these states and regions are reviewed as well as the real estate, labor, and tax policy all impacting the cost of doing business in a region followed by an analysis to review relevant infrastructure finance programs and economic development incentives.
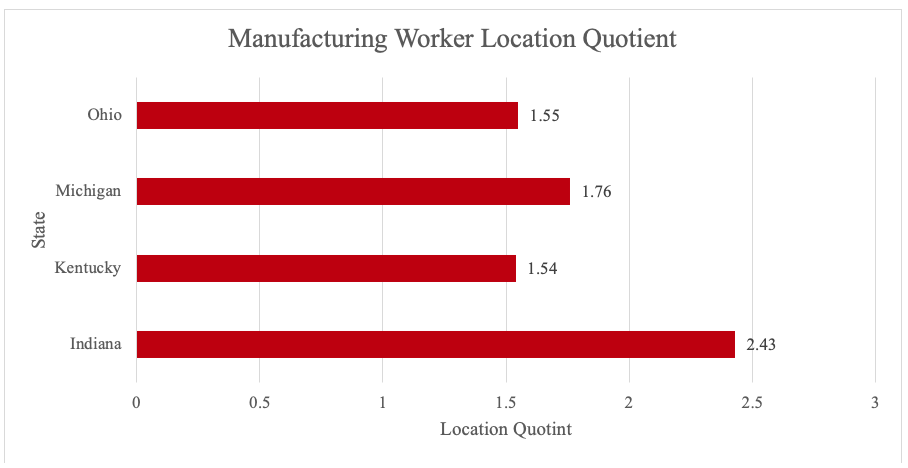
The table above illustrates the strength of the Midwest manufacturing industry and why this region should be attractive to global manufacturers.
Upon completion of this research, the company will then narrow its search to a handful of sites in multiple states and cities that fit the company’s business purpose. A confidential Request for Proposal or project letter is then sent from a corporate site location consultant or legal counsel that outlines the nature of the corporate site location project and the specific needs of the company related to the site in question with specific infrastructure, workforce, incentive, and site needs. Site acquisition, land use entitlements, economic development incentives, and government compensation agreements are then negotiated. Defining the economic prospects, workforce capabilities and cost of doing business in multiple regions is the first step for companies considering an economic expansion.
Economic development incentives offered by local and state governments, and coordinated often by regional economic development groups, can play an important role in reducing the costs of doing business in a market. Ohio and Kentucky offer two examples of economic development incentives worthy of review.
Kentucky, Ohio, and Virginia all offer compelling opportunities for a range of industries considering these states for a corporate site location project.
Kentucky Business Incentives. The Commonwealth of Kentucky offers a range of economic development incentives tied to the creation of new high-wage jobs and capital investment.
-
- Kentucky Business Investment (KBI) Program offers income tax credits and wage assessments for new and expanding businesses in sectors like manufacturing, headquarters operations, and technology-related services. Enhanced incentives are available for projects in certain counties.
- Kentucky Enterprise Initiative Act (KEIA) provides sales and use tax refunds on construction materials, equipment used in research and development, and data processing for approved projects.
- Direct Loan Program supports business expansion with below-market interest rate loans, available for non-retail projects in industries such as agribusiness, tourism, and manufacturing.
- Industrial Revenue Bonds (IRB) allows financing for manufacturing projects, healthcare facilities, and other significant ventures through bonds issued by state governments.
- Community Development Block Grants (CDBG) Loans offer federally funded low-interest loans through the Department for Local Government for community development projects.
- Kentucky Reinvestment Act (KRA): Job Retention program provides tax credits to existing Kentucky companies engaged in manufacturing, agribusiness, non-retail service or technology activities, headquarters operations, hospital operations, coal severing and processing, alternative fuel, gasification, energy-efficient alternative fuels, renewable energy, or carbon dioxide transmission pipelines permanently for a reasonable period that will be investing in eligible equipment and related costs of at least $2,500,000 for owned facilities and $1,000,000 for leased facilities (excluding rent).
- Bluegrass State Skills Corporation Workforce Program offers tax credits and grant reimbursements for employee training.
- Tax Increment Financing (TIF) supports public infrastructure improvements through future tax gains, with several programs tailored to both state and local development projects.

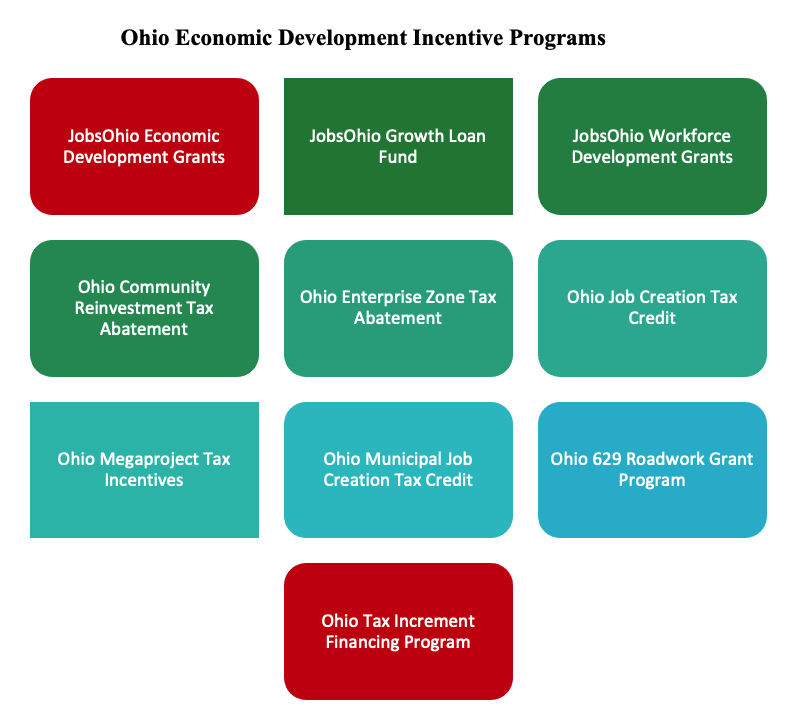
Ohio Economic Development Incentives. Ohio offers a wide range of economic development incentives at the local and state government level as listed below.
Ohio Economic Development Incentive Programs
-
- Jobs Ohio Economic Development Grant promotes development, business expansion, and job creation by providing funding for eligible projects in the State of Ohio.
obsOhio Workforce Grant was created to promote economic development, business expansion, and job creation by providing funding for the improvement of worker skills and abilities in the State of Ohio. The program requires job creation and training of employees within a specified period and may consider the amount of proceeds per job created and employee trained. JobsOhio may consider aiding for eligible projects that improve operational efficiencies or production expansion, along with the retention of jobs. - Ohio Community Reinvestment Area program is an economic development tool administered by municipal and county governments that provides real property tax exemptions for property owners who renovate existing or construct new buildings. Community Reinvestment Areas are areas of land in which property owners can receive tax incentives for investing in real property improvements.
- Ohio Enterprise Zone Program is an economic development tool administered by municipal and county governments that provides real and personal property tax exemptions to businesses making investments in Ohio. The Enterprise Zone Program can provide tax exemptions for a portion of the value of new real and personal property investment (when that personal property is still taxable) when the investment is made in conjunction with a project that includes job creation.
- Ohio Job Creation Tax Credit is a refundable and performance-based tax credit calculated as a percent of created payroll and applied toward the company’s commercial activity tax liability awarded to companies creating at least 10 jobs (within three years) with a minimum annual payroll of $660,000 and that pay at least 150 percent of the federal minimum wage and final approval from the Ohio Tax Credit Authority is required.
- Ohio Mega Site program is designed to attract large-scale industrial, headquarters, office, and research and development projects for high-wage jobs for projects at least $1 B in fixed asset investment and $75 M in payroll are eligible to receive double the term for local tax abatements and the Ohio JCTC.
- Ohio Municipal Job Creation Tax Credit provides an income tax credit tied to the provision of agreed-upon high-wage jobs and capital investment in various Ohio cities.
Ohio Roadwork Development (629) funds are available for public roadway improvements, including engineering and design costs. Funds are available for projects primarily involving manufacturing, research and development, high technology, corporate headquarters, and distribution activity. Projects must typically create or retain jobs. - Ohio Tax Increment Financing (TIF) is an economic development mechanism available to local governments in Ohio to finance public infrastructure improvements and, in certain circumstances, residential rehabilitation.
- Jobs Ohio Economic Development Grant promotes development, business expansion, and job creation by providing funding for eligible projects in the State of Ohio.
Global companies have substantial market opportunities in the United States but making economic investments in the U.S. requires an understanding of a corporate site location process driven by state and local governments.