Taxes levied by local and state governments have a major impact on a company’s corporate site location decisions. Taxes by the state and local governments are a critical component of measuring the cost of doing business in a region. Different local and state governments tax businesses differently. What and how much local and state governments tax business is a policy decision not just to collect the revenues needed to pay for schools, roads, water, public safety, and other essential services but is also a public policy decision impacting a company’s corporate site location.
Source: Council of State Taxation
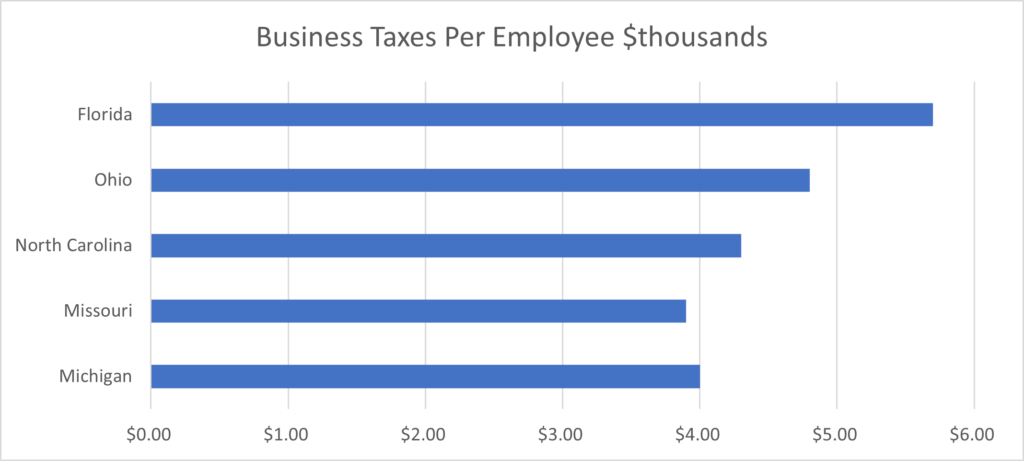
Ultimately, how much taxes a company pays at a location impacts its decision as to whether to locate in the region and defines the critical role of economic development incentives. The specific taxes a company will pay at a site is a critical cost of doing business factor the local and state government can directly impact through tax incentives. As the table below illustrates, companies in Michigan and Missouri pay a lower effective tax rate than companies in Florida, Ohio, and North Carolina. Michigan understands that lower effective tax rates on industry play a major role in the retention and expansion of private sector jobs.
Source: Council of State Taxation
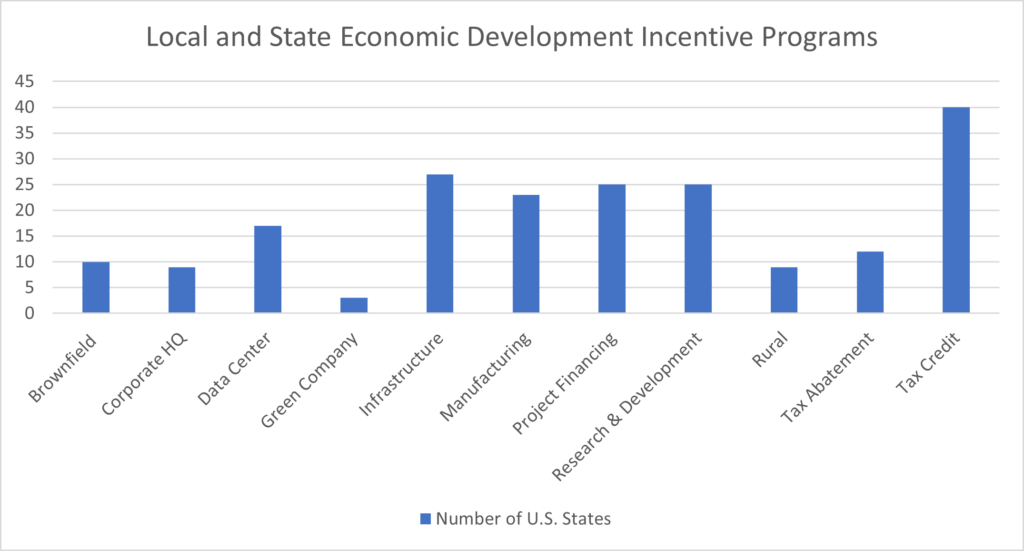
According to the Council of State Taxation, businesses paid $951.4 B in state and local taxes in FY21, which was 43.6% of all tax revenue at the state and local levels. Businesses paid $493.7 B in state taxes in FY21, which was 17.0% higher than the prior fiscal year, and $457.6 B in local taxes, which was 10.2% higher, for a combined year-over-year growth rate of 13.6% over FY20. To address regional cost of doing business factors, all fifty states offer some form of economic development incentives. As the chart below outlines, infrastructure incentives are provided by all the states in the union followed by tax credits as the second most popular tax incentive program in the nation with efforts to attract data centers and using general tax abatements tying for third. Princeton Economics estimates that state and local governments invest about $30 B dollars in economic development incentives annually.
Michigan offers a wide range of economic development incentives to companies considering the state for a corporate site location project. Tax credits are tools private developers, investors, and individual companies use to reduce tax burdens in exchange for economic growth. Tax credits may be either refundable or nonrefundable. A refundable tax credit, a moderate form of negative income tax, can reduce the tax owed below zero and result in a net payment to the taxpayer beyond its own payment into the tax system. A nonrefundable tax credit cannot reduce the tax owed below 0; thus, taxpayers do not receive a refund exceeding their payments into the tax system. Most state economic development tax credits are triggered by high-wage, non-retail job creation, and some level of capital investment. These tax credits in most cases are competitively awarded as there is a limited amount of state government funding available to support them. Thus, higher job growth, higher wage, and larger capital investments from companies attractive for investment are given priority for these tax credits.

The Michigan Business Development Program (MBDP) is the state’s prime economic development incentive program awarded by the Michigan Economic Development Corporation. The MBDP is a performance based economic development incentive that is available to eligible businesses that create qualified new jobs and/or make qualified new investment in Michigan.
MBDP Qualifications
| CATEGORY | STANDARD | RURAL | INNOVATION | MICRO |
| Qualified new jobs | 50 | 50 | 25 | A number of qualified new jobs acceptable to the Michigan Strategic Fund |
| Company Stage | Second | Second | Second | Second |
| Other Qualifications | None | County population less than 90,000 | The project must fall within an “innovation industry | Must meet one of the following: • MEDC “Strategic Focus Industry” or “Regional Impact Industry” • Located in a geographically disadvantaged area • Located in a community with less than 15,000 or more than 25,000 with unemployment greater than state average |
The MBDP is targeted to the key industries as listed in the table below.
MBDP Key Industry Targets

Michigan also offers the Critical Industry Program (CIP) to provides qualified investments to qualified businesses for deal-closing, gap financing, or other economic assistance to create or retain qualified jobs as a result of a technological shift in product or production or make capital investments, or both, in Michigan as determined by the MSF board. Administered by the MEDC on behalf of the MSF, this tool provides access to grants, loans, or other economic assistance.

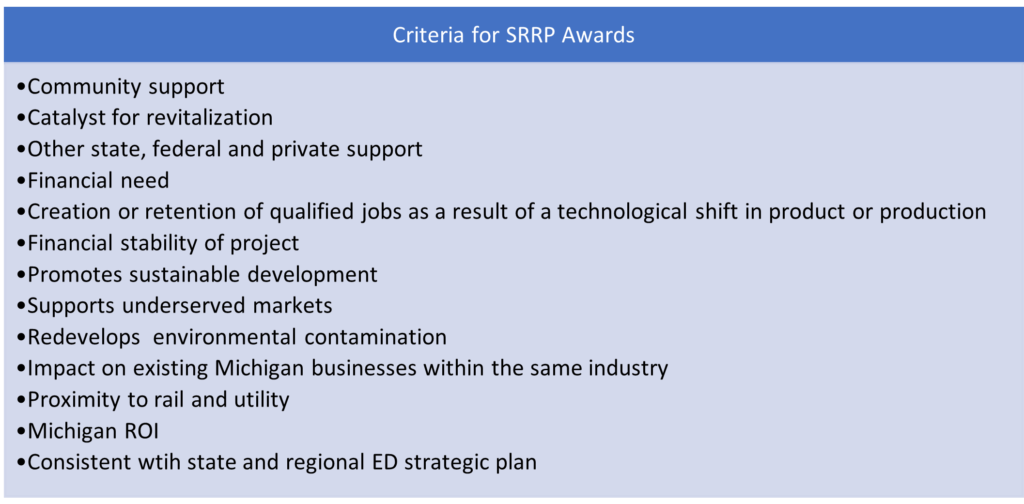
The Michigan Strategic Site Readiness Program (SSRP) provides financial incentives to eligible applicants to conduct eligible activities on, or related to, strategic sites and mega-strategic sites in Michigan, for the purpose of creating investment-ready sites to attract and promote investment in Michigan. Eligible activities of SRRP funding includes: land acquisition and assembly; site preparation and improvement; infrastructure improvements that directly benefit the site, including without limitation, transportation; infrastructure, water and wastewater infrastructure, and utilities necessary to service the site; any demolition, construction, alteration, rehabilitation, or improvement of buildings on the site; environmental remediation; and architectural, engineering, surveying, and other predevelopment work required to commence construction on site improvements; or to develop a spending plan and proposal for capital investment in site readiness.
The availability of industrial sites is a key corporate site location issues facing nearly every state in the Union. Tennessee’s successful Mega Site Program has spurred states like Michigan and others to address the need for major industrial site development in preparation for large scale job producing centers.

The Jobs Ready Michigan program was created by the Michigan Strategic Fund to meet the talent needs of companies that are expanding or relocating to Michigan. The program is designed to be flexible and responsive to the specific talent needs of companies and to address the costs associated with recruiting and training individuals for occupations that are high-wage, high-skill, or high-demand.

To attract new businesses and encourage the expansion of existing businesses, state and local governments also may offer tax abatements as an economic development incentive. Tax abatements temporarily decrease the amount of taxes a business owes. While this tax incentive has a general effect on property taxes, the means employed by state and local governments to achieve this effect varies from program to program. Michigan’s State Essential Services Assessment (SESA) Exemption Projects located in eligible distressed areas (EDAs) that result in $25 million or more of qualifying investments in eligible manufacturing personal property may be considered for a State Essential Services Assessment (“SESA”) exemption. Projects that are not located in a distressed area that result in $25 million or more of qualifying investment in eligible manufacturing personal property may be considered for an Alternative SESA if the MSF board determines the project, is a transformational project.

The MSF will consider the following factors when reviewing a SESA Tax Exemption project:
• Out-of-state competition
• Net-positive return to this state
• Level of investment made by the eligible claimant
• Business diversification
• Reuse of existing facilities
• Near-term job creation or significant job retention as a result of the investment made in eligible personal property
• Strong links to Michigan suppliers.
Michigan has no shortage of economic development incentive programs designed to support the retention and attraction of high-wage jobs and capital investment; however, it is critical for companies seeking these incentives to understand the criteria in which the Michigan program funds are awarded.